Blockchain in Education
Blockchain in Education
Blockchain in Education
1. Definition
Volpicelli (2016) defined blockchain as “shared or distributed or decentralized digital ledgers which use cryptographic algorithms to verify the creation and transfer of digitally represented assets or information over a peer-to-peer network”. In 2008, when Bitcoin first appeared, the term blockchain, back then used as "block chain" was glued to the Bitcoin digital currency. It wasn't until Ethereum introduced their Smart Contracts in 2015, that blockchain was finally released from its exclusive tie to Bitcoin, and went on to be adopted by other sectors like healthcare and education. Blockchain provides a decentralized, distributed public and trusted ledger upon which two parties can perform transactions without necessarily trusting each other, and without reliance on a central third party. (Oyelere et al., 2019).
2. Characteristics of Blockchain Technology
Traceability is the ability to track a specific transaction within the blockchain network. Inspecting the block detailed information of each transaction will reveal useful facts for tracking the transaction, since blockchain are time-order arranged, and each block is connected with the other closeby blocks.
Transparency permits all members within the blockchain to control the transactions since transactions are broadcasted and publicized as at when inputted. It is possible for members within the network to detect and reject distrustful transactions, thereby creating a sense of openness, transparency and security. Information on the blockchain cannot be altered without the consent of other participants, therefore building mutual trust, reliability and durability against internal or external attacks.
Decentralization allows the delivery of data processes such as input, transmission, verification, update, storage on the blockchain network are established according to the distributed structure. This ensure that the risk and responsibility of program execution and data processing are transferred from centralised systems to decentralized blockchain networks, where the trust between the network nodes are established through strong encryption and decryption techniques.
Immutability property ensure that the data and logs of transactions that are created mutually within the blockchain network are consistent at all times. Therefore, validated transactions or committed blocks cannot be modified or deleted.
3. Advantages of Blockchain technology
From the aforementioned characteristics of blockchain, we can derive some advantages of using blockchain in education.
Reliability: The failure of a single node in the network will not affect the whole network thanks to the decentralization characteristic of a blockchain network. This avoidance of single infrastructural point of failures allows the system higher reliability as opposed to centralized ledgers.
Trust: Instead of few institutions in charge of educational data, the trust of which we usually take for granted, blockchain technology allows all the nodes in the network to act as trust bearers with decentralized ledgers.
Security: The use of the hash function, which change a variable-length string into a fixed-length binary sequence halts any apparent relationship between the input and the output. The process is hard to reverse as it is impossible to trace back to the variable-length input from the binary output. This adds up to the newly generated nodes having to follow a linear sequence of time in the chain.
Efficiency: All data added to the blockchain undergoes a set of predefined procedures, this results in reducing the labor time as the number of involved intermediaries is reduced, which subsequently improves efficiency.
Authenticity of documents and certifications: All transaction within the blockchain network are legal and protected against fraudulent manipulation. Therefore, educational documents such as certificates, transcripts, and skills records are authenticated and validated.4. Blockchain-based Educational Solutions
Table 1 below shows the existing systems (majority of which are designs and not implementations) that harness the power of blockchain in education.
Table 1. Existing solutions of blockchain in education (Oyelere et al.,2019)
Author(s) | Type of blockchain technology or blockchain Platform | Solution |
Alexander Mikroyannidis, John Domingue, Michelle Bachler and Kevin Quick (2018) | Smart Contracts | The European Data Science Academy (EDSA) investigates the use of Smart Blockchain Badges to support in advancing the data science career of their learners. It issues badges into the blockchain containing information on data science courses completed (or partly completed) and skills acquired by the learners. |
Cheng, Lee, Chi, & Chen, (2018) | Smart Contract for Digital Certificate | A solution to the problem of forged certificates based on blockchain technology. The system provide digital certificate with anti-counterfeit, anti-fraud, authenticity, and verifiability. The solution also use QR-code and inquiry string code attach to the paper certificate. |
Sony Global Education (2017) | IBM Hyperledger (Smart Contracts) | The solution allows school administrators to manage students' educational data from several schools, as well as their records and digital academic transcripts with more trustworthiness. |
MIT Media Lab, Learning Machine (2015) | Smart Contracts | This open source project focuses on developing the required technical resources for developers to use in their blockchain projects, rather than providing custom implementations. |
Ocheja, Flanagan, & Ogata, (2018) | Blockchain Based Learning Analytics Platform | Proposed a blockchain based approach for connecting learning data across several learning platforms, institutions and organizations |
Han et al. (2018) | Smart Contracts | Proposed a blockchain-based technique for creating an environment where individuals can be the owners of their official education records and can easily share those records. |
Farah et al. (2018) | Tamper-Evident Learning Trace Repositories | The application of smart contract technology for developing an architecture that uses blockchain technology to sign and validate learning traces for authenticity. |
Gilda, & Mehrotra (2018) | Blockchain for Student Data Privacy and Consent | A solution based on smart Contracts, hyperledger fabric and hyperledger composer, to develop a nested authorization that permits a data administrator to grant authorization rights for educational consent rights. |
Forment, et al. (2018) | Smart Contracts | Discusses the need of privacy in learning analytics contexts, and suggests the reliance on blockchain or smart contracts to support in such mission. The solution that has yet to be implemented is a software that can run along with Moodle LMS. (The proposed solution is not yet implemented but is part of an ongoing PhD project at the university of Salamanca, Spain). |
Arenas & Fernandez (2018) | CredenceLedger | The study present a decentralized verification of academic credentials based on blockchain. The system stores compact data proofs of digital educational credentials for easy verification. |
Turkanovic, et al. (2018) | Suggests and provides a first prototype of EduCTX, an alternative to European Credit Transfer and Accumulation System (ECTS) based on the blockchain technology. A higher education credit, and grading system offering a globally unified viewpoint for students and higher education institutions. | |
Wu & Li (2018) | Blockchain based Digital Education Operational Skill Competition System | A blockchain based competition mode Application to support gaining operational skill. |
Liu et al. (2018) | Hyperledger - Education-industry cooperative system | This system is in prototype phase, uses IBM's hyperledgers and implements a blockchain-based education-industry cooperative system where students share data with employers. |
Duan, Zhong, & Liu, (2017). | Learning outcome and meta-diploma solution | The study focused on the blockchain technology based on learning outcome. |
John Rooksby & Kristiyan Dimitrov (2017) | A blockchain system based on Ethereum | Exploratory design and implementation of blockchain system for use at the university to store student grades |
Hölbl, et al. (2018) | EduCTX, Managing Digital Micro-credentials based on ethereum | An ethereum based platform that enables managing, assigning and presenting credentials for educational stakeholders |
Gazali, et al. (2018) | Smart Contracts, Ethereum | Dedicated to student loans, it can help the Malaysian National Higher Education Fund Corporation (PTPTN) better track the status of borrowers and collect back their payments. The borrowers are able to track their transactions and current arrangements with multiple organizations in the platform. |
Jirgensons & Kapenieks (2018) | OpenBlockChain | An ethereum based blockchain platform created by UK’s Open University Knowledge Media Institute (KMI) |
Shen & Xiao (2018) | Online quiz scheme based on Double-layer Consortium Blockchain | The online quiz system help to solve the problem of non-transparent scoring process by providing open verification of the test records. |
Farah et al. (2018) | Smart Contracts | Another application of blockchain in learning analytics. It suggests a blueprint for a system that uses blockchain technology to validate the authenticity of learning traces from online learning activities which are stored across multiple locations. |
Bai et al. (2018) | Smart Contracts | The system proposed here is called Researchain. A system that helps in Scientific Project Research Management SPRM. |
Note that for this module's learning activity (LA 4), you can refer to one of these blockchain-enabled educational solutions and reuse it for your chosen learning environment.
5. Example: Ocheja's Blockain-based Learning Analytics Solution
Ocheja identified 3 main limitations on LA solutions:
• Connecting learning histories of a learner on different learning platforms on a single immutable trail.
• Ensuring privacy of learners’ records with ease of access control.
• Integrating research and production systems for advancing learning.
Ocheja suggested a shift from a traditional learning systems platform architecture to one where blockchain is used to ensure privacy and authenticity of learning records and data used in LA.
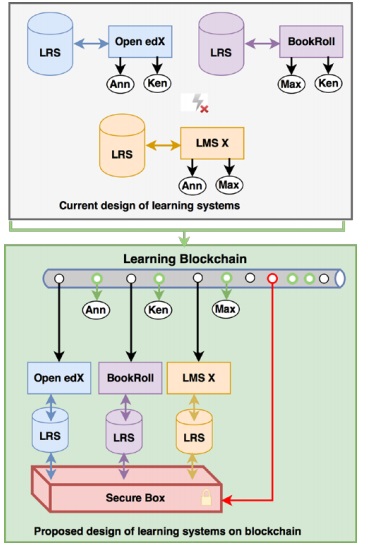
Fig1. Proposed learning systems architecture (Ocheja et al., 2018)
Application of Blockchain in Education - OpenBadges
Types of badges, and how to define badgeshttps://www.usf.edu/career-services/documents/webinars/basics-of-badging.pdf
Example of badge architecture for SELI platform
References
Blockchain technology and gamification - conditions and opportunities for education Jaroslav Veteška (ed.). Adult Education 2018 – Transformation in the Era of Digitization and Artificial Intelligence. Praha/Prague, 2019
Connecting decentralized learning records: A Blockchain Based Learning Analytics Platform. Ocheja, Patrick; Flanagan, Brendan; Ogata, Hiroaki. Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Learning Analytics and Knowledge (2018): 265-269